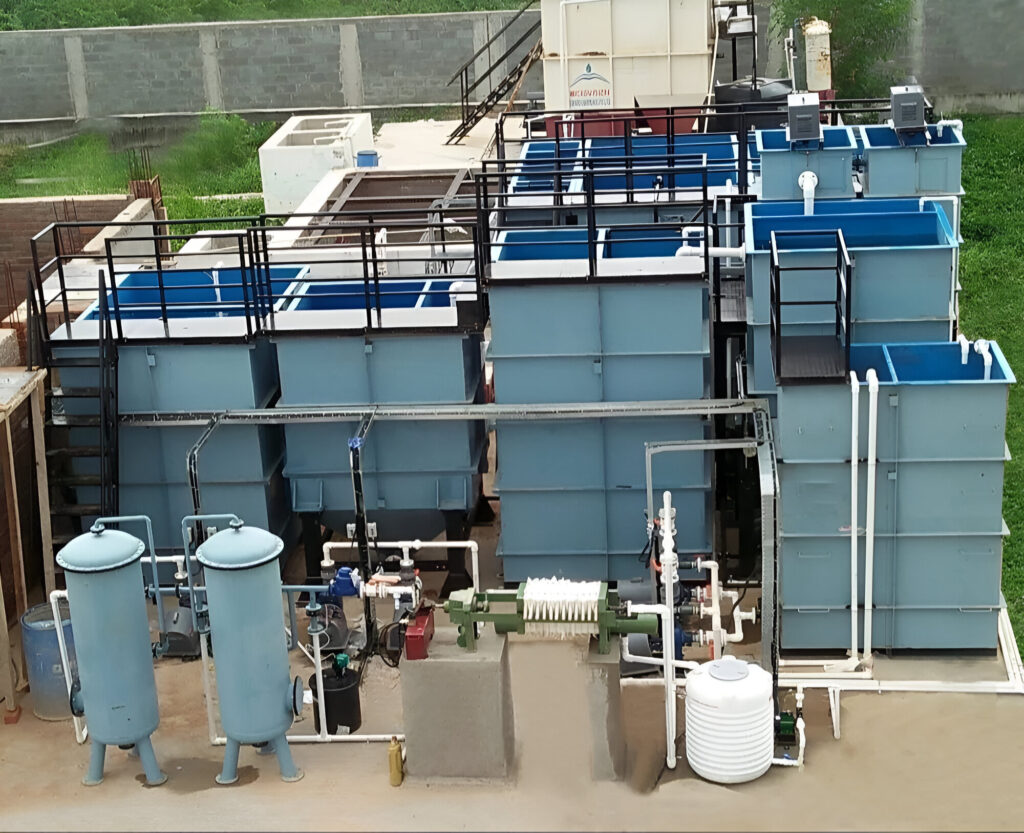
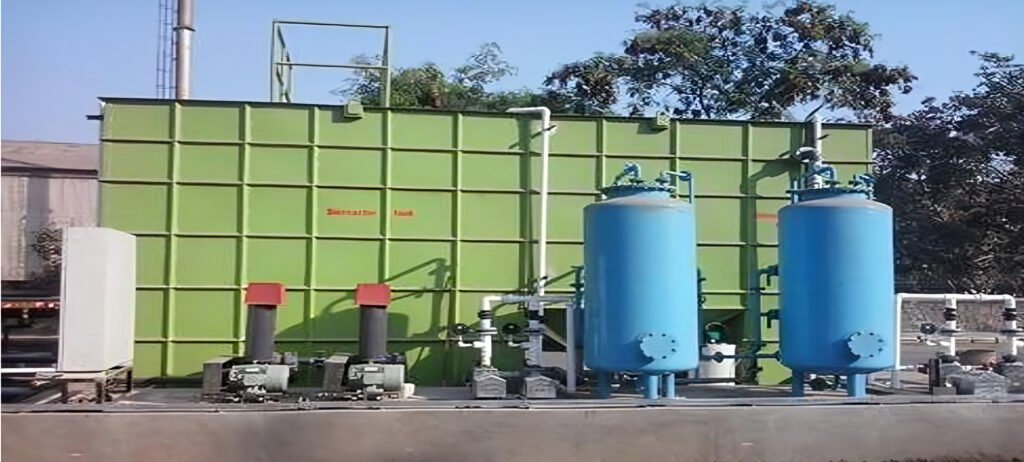
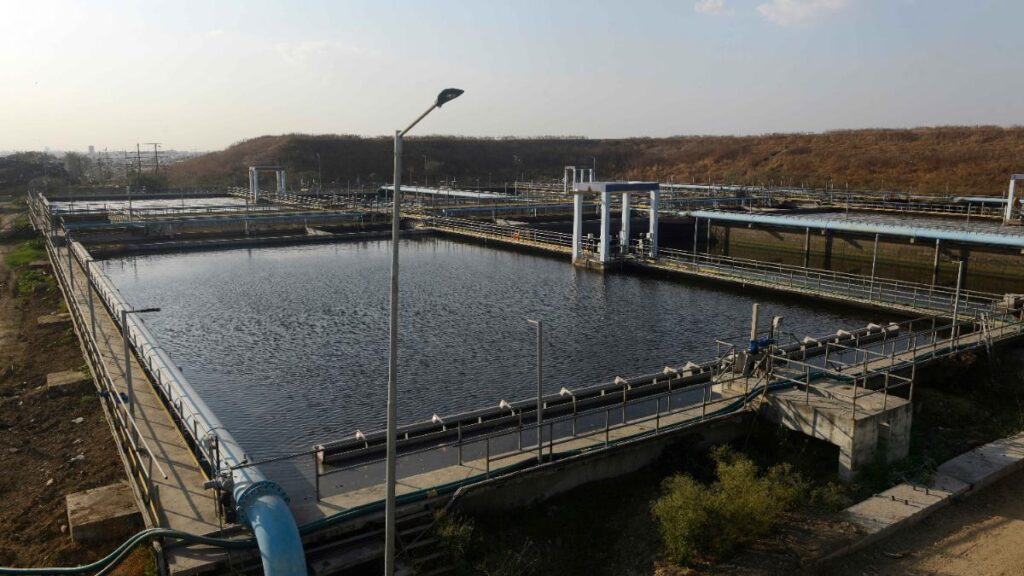
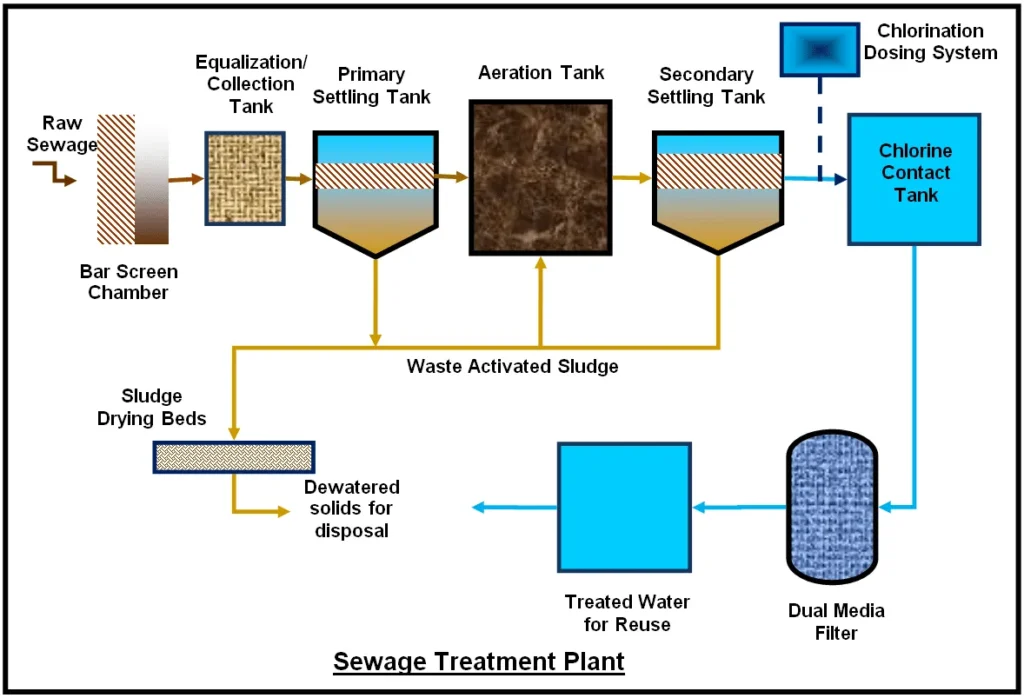
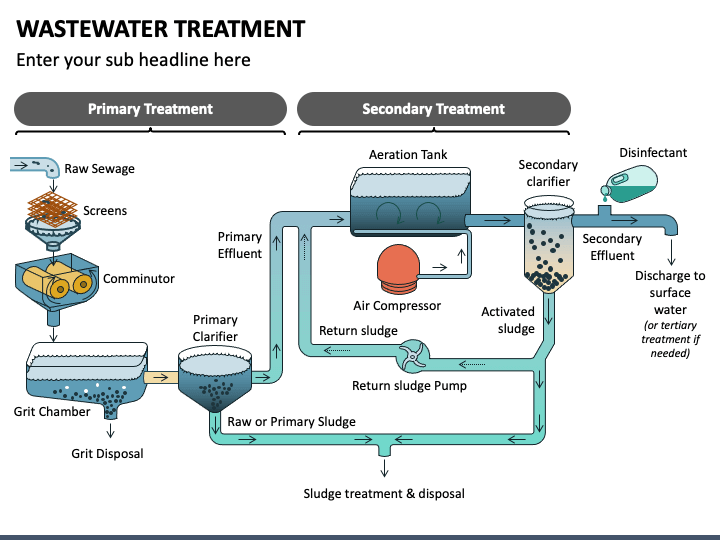
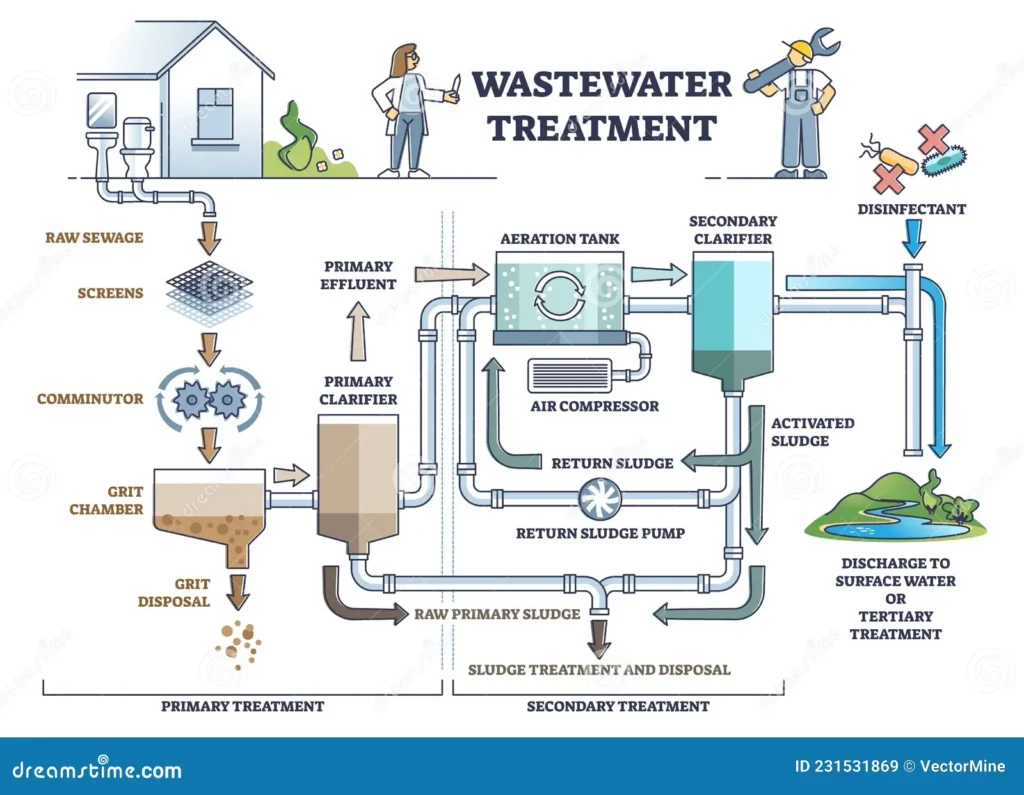
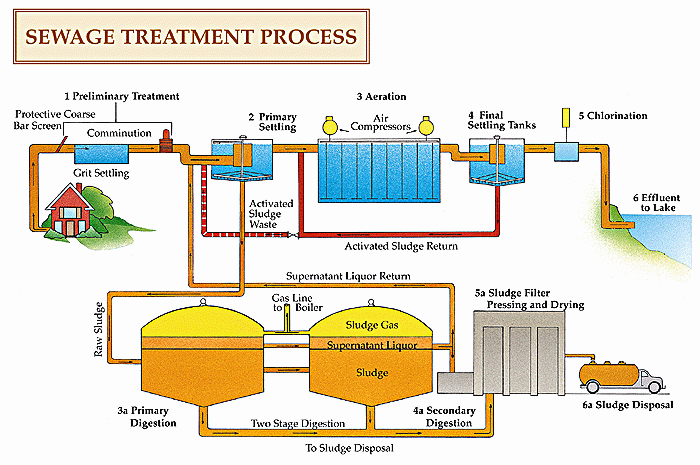
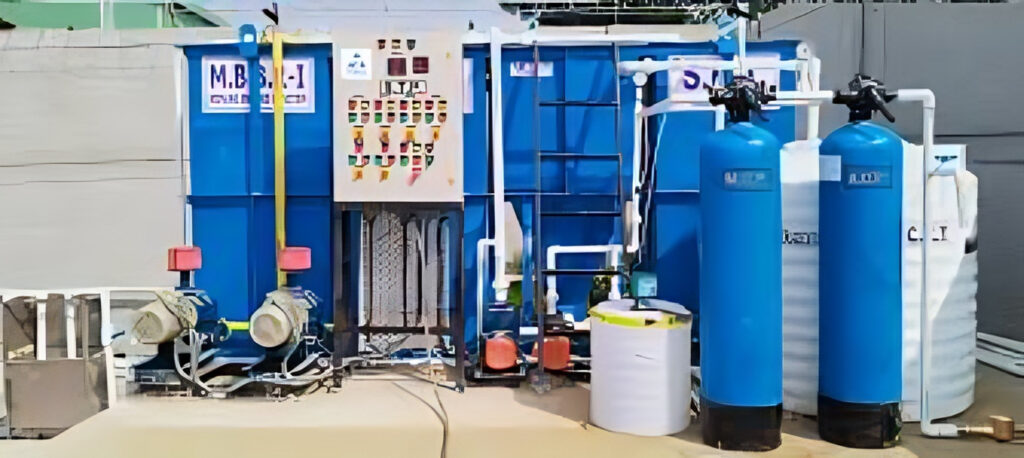
A Sewage Treatment Plant (STP) is a critical infrastructure designed to treat and purify wastewater from domestic, commercial, and industrial sources before it is discharged back into the environment or reused. The primary objective of an STP is to remove contaminants, harmful microorganisms, and pollutants from sewage, thereby ensuring the treated water meets regulatory standards for safety and cleanliness. The treatment process typically involves multiple stages, including preliminary treatment to remove large debris, primary treatment for sedimentation of suspended solids, secondary treatment utilizing biological processes to decompose organic matter, and tertiary treatment for advanced purification through filtration, chemical processes, and disinfection. By effectively managing and treating wastewater, STPs play an essential role in protecting public health, preserving aquatic ecosystems, and promoting sustainable water resource management
What are the fundamental reasons for the necessity of Sewage Treament Plants(STP’s)?
Sewage treatment plants (STPs) are indispensable infrastructural components vital for safeguarding public health and preserving the environment. By effectively removing harmful pathogens, chemicals, and pollutants from sewage, STPs play a pivotal role in preventing the spread of diseases and maintaining the integrity of water ecosystems. Moreover, stringent regulations mandate the treatment of sewage to meet specified standards before discharge, ensuring compliance and safeguarding water quality. Beyond mere compliance, STPs offer opportunities for resource recovery, including water, nutrients, and energy, thus contributing to sustainable resource management. This sustainable approach not only minimizes environmental impact but also promotes community well-being by providing access to clean water for various purposes. In essence, STPs are indispensable for mitigating pollution, conserving resources, and enhancing the overall health and sustainability of communities and ecosystems.
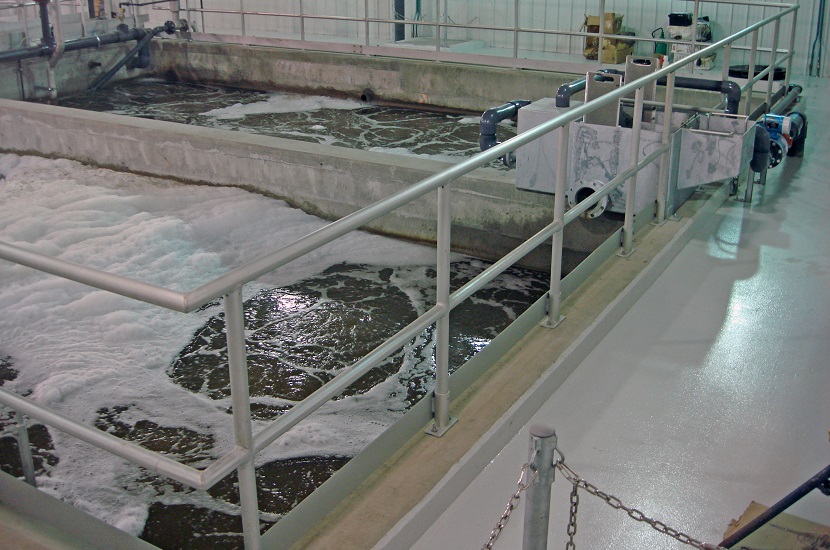

Aeration Tank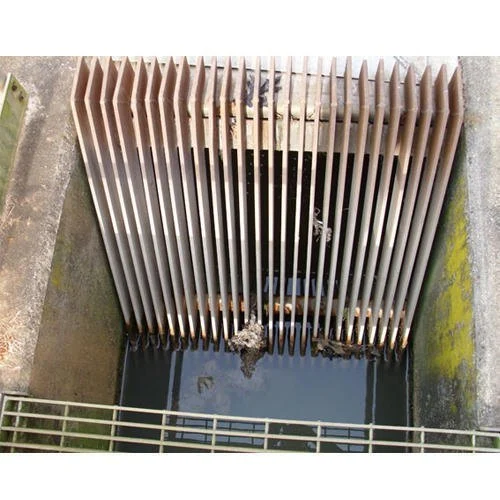 
Bar Screen Chambar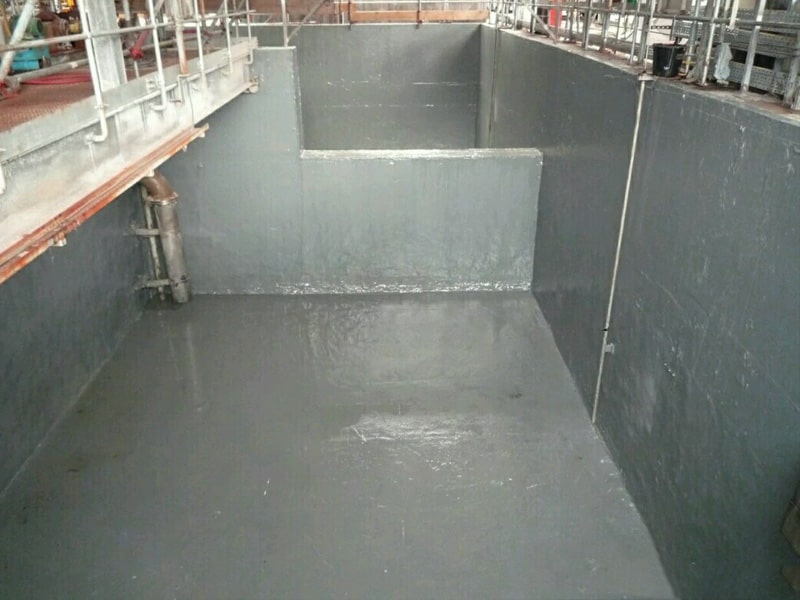 
Raw Water Tank 
Sludge Holding Tank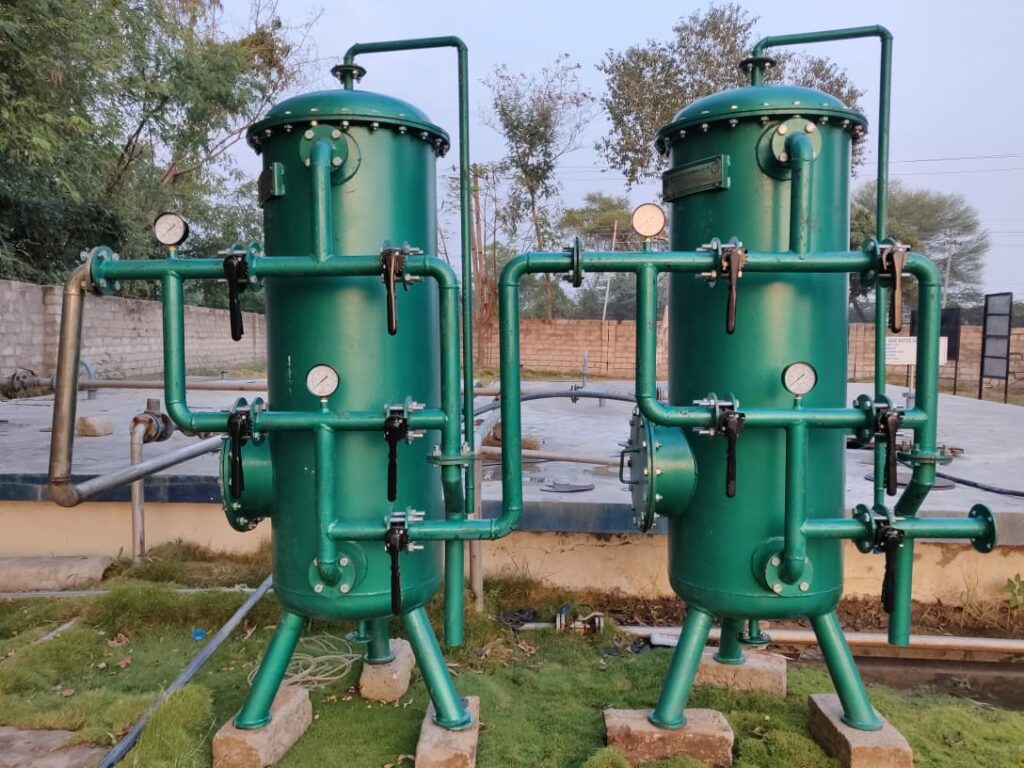 
Sand_Carbon_filter
How many different technologies are we providing for Sewage Treatment Plants (STP)?
Sequencing Batch Reactor (SBR)
Sequencing Batch Reactors (SBR) are a type of activated sludge process for wastewater treatment in which wastewater is added to a single “batch” reactor, treated to remove undesirable components, and then discharged. SBR systems are designed to handle the variation in influent flow and load, making them highly flexible. The process includes filling, reacting, settling, decanting, and idling phases, all occurring in the same tank. SBRs are known for their high efficiency in removing organic matter, nitrogen, and phosphorus, making them suitable for both municipal and industrial wastewater treatment.
Membrane Bioreactor (MBR)
Membrane Bioreactors (MBR) combine conventional biological treatment processes with membrane filtration. MBR systems use micro or ultrafiltration membranes to separate treated water from suspended solids. The key advantages of MBRs include a smaller footprint compared to conventional systems, the ability to produce high-quality effluent that can be directly discharged or reused, and enhanced removal of pathogens and micropollutants. MBR technology is particularly beneficial in areas with stringent discharge regulations or where water reuse is a priority.
Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR)
Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors (MBBR) utilize thousands of small, specially designed plastic carriers within the aeration tank to create a large surface area for biofilm growth. The carriers move freely in the wastewater, facilitating effective contact between the waste and the microorganisms. This technology enhances the degradation of organic matter and nutrients without the need for sludge recycling, making it simpler to operate and maintain. MBBR systems are highly effective in treating high-strength industrial wastewater and are adaptable to existing treatment plants to increase capacity and efficiency.
Constructed Wetlands
Constructed wetlands are engineered systems designed to mimic the treatment processes occurring in natural wetlands. These systems use vegetation, soil, and microbial activity to treat wastewater. There are two main types: surface flow wetlands, where water flows over the soil surface, and subsurface flow wetlands, where water moves through a gravel or soil medium planted with vegetation. Constructed wetlands offer a sustainable, low-energy option for wastewater treatment, providing effective removal of pollutants such as suspended solids, organic matter, nutrients, and heavy metals. They also offer additional benefits such as habitat creation and landscape enhancement.
Experience
Srinivasa Engineering and Enviro Solutions is a distinguished firm specializing in sewage treatment plant services and maintenance. Founded in 2012 by Sanam Venkat Ramesh and Jana Venkateshwar Rao, the company boasts over three decades of extensive industry experience.
Background
Srinivasa Engineering & Enviro Solution is a distinguished entity in the field of wastewater management, demonstrating a steadfast commitment to environmental sustainability and technological innovation. Founded in 2012, the company has leveraged decades of industry expertise to establish itself as a trusted provider of sewage treatment plant services. Under the visionary leadership of Managing Director Sanam Venkat Ramesh, who brings over 30 years of experience, the company has achieved significant milestones in the industry. Partner Jana Venkateshwar Rao adds further depth to the leadership team, ensuring the delivery of cutting-edge solutions and exceptional service quality.
Srinivasa Engineering & Enviro Solution is dedicated to addressing the complex challenges of wastewater management, serving 65 prominent clients in Hyderabad and employing a skilled workforce of over 210 professionals. Their comprehensive approach encompasses the design, operation, and maintenance of advanced sewage treatment technologies, reinforcing their reputation for excellence and reliability in the sector.